Table of Contents
Let a cardiologist interpret your ECG
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a simple and important informative method for diagnosing the cardiovascular system.
On the curved lines of the cardiogram, there are special elements corresponding to certain stages of the heart.
To understand the ECG readings, you need to know what exactly the electrocardiograph records.
The electrocardiogram records the electrical activity of the heart, which cyclically changes during the period when the heart cavity is free of blood (systole) and during its filling (diastole).
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in humans today. Modern methods of diagnostics of various pathologies make it possible to reduce mortality.
One of these methods is ECG (electrocardiogram) – the determination of heart rate indicators. This examination is very simple, non-invasive (non-tissue traumatic) and informative.
As part of the diagnosis, the activity of the heart muscle is recorded. The results of the study are recorded on a paper tape and can be immediately evaluated by a doctor.
When ECG is diagnostics assigned?
It is recommended to make an ECG for patients when:
- Severe chest pain
- Shortness of breath even at rest
- Persistent dizziness and fainting
- Physical intolerance
Heart murmurs detected during primary diagnosis.
Also, the study is carried out with high blood pressure (constant or intermittent), heart rhythm disturbances, rheumatism, diabetes mellitus.
An ECG is performed in case of an overdose of certain medications.
Part of the mandatory examination is an electrocardiogram when:
- Pregnancy. Diagnostics is necessary in connection with a change in the circle of blood circulation
- Assessment of a person’s professional suitability
- Standard clinical examination
- Preparing for surgery
There are other indications for an ECG. You can get a referral for an electrocardiogram from your doctor or make an appointment yourself.
OUR TOP PICKS OF ECG MACHINES
How to decipher the diagram of the work of the heart?
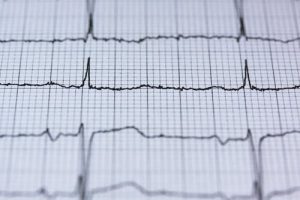
The work of the heart muscle on the cardiogram is presented as a continuous line with alphanumeric designations and various marks.
The ECG transcript plan includes an analysis of the entire resulting graph, which can only be performed by a specialist.
Correctly “read” the results are capable not only of cardiologists, but also therapists and paramedics. Often, not only the health, but also the life of the patient depends on the timely decryption of all data.
When analyzing data, experts pay attention to such important indicators as:
- Intervals
- Barbs
- Segments
Important! There are quite strict indicators of the ECG norm, in some cases even the slightest deviations may indicate violations of the heart muscle. But only a doctor can rule out or confirm a pathology
This is due to a number of factors:
- Cardiogram readings in certain conditions (for example, during pregnancy) may differ from the norm, but do not indicate the presence of a disease
- It is impossible to draw conclusions on individual indicators. Decoding is carried out only in a comprehensive manner and includes an assessment of all parameters
- In some cases, only the results obtained under certain conditions (under load, in dynamics, etc.) are informative.
Do not try to compare different studies with each other and do not draw conclusions from separate data.
Entrust this job to professionals! So you are guaranteed to get the correct diagnosis and you will not be afraid of pathologies that you actually do not have.

Cardiograms readings. ECG norms
A normal electrocardiogram of a healthy person looks like this:
- Heart rate: in the range from 60 to 80 beats per minute
- Heart rate type: sinus
- RR Interval: 0.6-1.2 sec
- PR interval: 120-200 milliseconds
- ST interval: 320 milliseconds
- QT interval: 420 milliseconds or less
- P-wave – 80 milliseconds
- T-wave – 160 milliseconds
- J-wave: absent
Note! The rates are indicated for an adult! In children, they are different.
Pathologies
During the removal of the electrocardiogram, the following violations can be detected:
Sinus arrhythmia. In some cases, it is the norm in children and young adults. Such a rhythm in pathology indicates physiological disorders. Sinus arrhythmia requires observation by a cardiologist, especially in cases where the patient has a predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Sinus bradycardia. This pathology is characterized by a heart rate of about 50 beats per minute. This bradycardia also occurs in healthy people during sleep, as well as in athletes.
Extrasystole. This defect in rhythm manifests itself in a chaotic, too frequent or infrequent heartbeat. Patients may complain of unpleasant tremors behind the breastbone, tingling, a feeling of emptiness in the stomach, a feeling of sudden fear.
Sinus tachycardia. With this pathology, the heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute. It can occur during physical or emotional stress and in healthy people.
Also, sinus tachycardia accompanies the intake of alcoholic beverages, energy drinks and strong coffee. In these cases, it is temporary. With pathology, patients complain of periodic heartbeats even at rest and not while taking certain drinks.
Paroxysmal tachycardia. This condition is characterized by a rapid heartbeat. An attack occurs, which lasts from several minutes to several days. At the same time, the pulse can exceed 200 or even 250 beats per minute.
WPW syndrome. It is a subtype of supraventricular tachycardia and is characterized by an increased heart rate and feeling of shortness of breath, cardiac sinking, and palpitations. Also, pathology is characterized by fainting, shortness of breath, dizziness.
CLC. With such a pathology, patients complain of a rapid heart rate.
Atrial fibrillation. This disease can be both permanent and intermittent. Patients with atrial fibrillation complain of severe flutter of the heart, feel anxiety and even panic.
Other pathological conditions are also distinguished.
All of them require observation by a cardiologist and regular full examination, which includes not only an ECG, but also other studies.
Often, an accurate diagnosis of a patient can be made only after evaluating a number of indicators obtained after laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Where do you take cardiogram?
An electrocardiogram can be taken at any medical facility that has a therapist and cardiologist. The patient lies down on the couch, the doctor fixes the electrodes and turns on the electrocardiograph.
During the recording of the cardiogram, a person must observe absolute calmness, the manifestation of any stimuli that can distort the real work of the heart is unacceptable.
Having received the cardiogram record, the doctor analyzes and deciphers it, then displays all identified pathologies and deviations from the norm in the final report.
An electrocardiograph recording an ECG can be single-channel or multi-channel, and the speed and quality of the recording depends on its functionality.
Modern devices are connected to a computer and, with the help of a special program, at the end of the session, they immediately issue a ready-made conclusion.