Table of Contents
Ear Infections and Hearing Loss
An ear infection occurs when a bacterial or viral infection affects the middle ear, one of the regions behind the eardrum. Ear infections can be painful due to inflammation and fluid buildup in the middle ear.
Ear Infections and Hearing Loss
Ear infections can be chronic or acute. Acute ear infections are painful but of short duration.
Chronic ear infections are painless and recur many times. Chronic ear infections can permanently damage the middle and inner ear, resulting in surgery.
Causes and risk factors of Ear Infections and Hearing Loss
Acute ear infections develop when the Eustachian tube (the canal that connects the middle ear to the pharynx) becomes clogged.
In children, this channel is much narrower than in adults, therefore, their inflammatory processes develop more often.
Chronic ear infections are caused by prolonged or recurrent acute inflammation.
Ear infections can be caused by:
- Bacterial infection;
- Cold;
- Flu.
The risk factors for chronic ear infection are as follows:
- Recent upper respiratory tract infection;
- Down syndrome;
- Genetic predisposition
Examination and diagnosis of Ear Infection
In order to identify acute inflammation of the middle ear, to diagnose acute otitis media, the otolaryngologist should examine the eardrum, nasopharynx, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
In some cases, it is necessary to check the patient’s balance and coordination of movements in order to timely identify possible consequences of the disease, for example, labyrinthitis with toxic damage to the inner ear.
In this case, research methods such as tympanometry, threshold audiometry, sound audiometry are used.

The diagnosis also includes hearing tests. Auricle discharge is often analyzed.
In case of suspicion of complications, for example, mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone) or other side effects, an X-ray examination is performed.
With the help of an X-ray, the results of a computed tomography of the temporal bone or cranium, it is possible to determine the expediency of surgical intervention in a timely manner.
Treatment Of Ear Infection
The American Academy of Otolaryngology does not recommend the use of antibiotics, antihistamines, and anti-inflammatory supplements for the treatment of otitis media.
However, they are indicated for the treatment of acute ear infections.
Treatment of an ear infection includes:
At the initial stage of the disease, it is recommended to use decongestant nasal sprays.
Additionally, the intake of anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and pain relievers of natural origin is prescribed.
- Dry clean. This is a procedure in which the doctor cleans the ear from impurities and exudate;
- Supplement treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory supplements. It is important to remember that acetylsalicylic acid is contraindicated in children;
- Antibiotics are indicated when bacteria are the cause of the ear infection. For patients with chronic inflammation, they may not be effective; Antibiotic treatment is prescribed by your doctor to prevent serious complications from otitis media and to reduce the risk of otitis media.At the same time, it is important to strictly follow all instructions regarding the frequency and duration of antibiotic use.
- The use of antifungal agents is recommended for fungal infection of the ear;
- Tympanocentesis, or “ear tap”, is a procedure in which fluid is removed from the eardrum for bacteriological examination. If the ear infection does not respond to treatment, the doctor may place a pressure tube in the eardrum to compensate for the pressure;
- Removal of adenoids. Adenoids are glands in the back of the nose that are responsible for killing infection.
With prolonged inflammation, they can increase significantly in size, which leads to ear infections and accumulation of exudate. In the case when such processes are often repeated, the doctor can remove the adenoids.
Prevention of Ear Infections and Hearing Loss
The following tips can help prevent recurrence of chronic ear infections:
Avoid contact with cigarette smoke. Heavy and passive smoking irritates the Eustachian tube, which increases the risk of ear infections.
Use ear sticks with extreme caution, as they can cause injury and disrupt the natural cleansing mechanism in the ear canal.
Hearing Loss and Ear Infection
Cases of hearing loss fall into two broad categories: first, congenital disorders, in which hearing loss occurs from birth; they are caused, for example, by genetic disorders or premature birth.
The second category is acquired disorders, in which hearing loss develops after birth and is the result of factors such as illness or injury to the ear.
Although we actually “hear” with the brain, hearing loss occurs when some part of the ear – the outer, middle, or inner – is damaged by infection or by genetic disorders or not functioning properly, and as a result, the ear cannot transmit normal sound signals to the brain
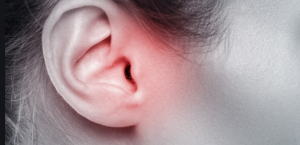
Remember, that some inflammatory processes in the ear can go away on their own. However, if the symptoms have not disappeared within 3 days, you need to see a doctor who can choose the right treatment depending on the type of your ear infection.
Ear Infection caused by a foreign body?
From a medical point of view, a foreign object is an object which inside in your body, but does not belong to it.
Foreign objects can enter the body by accident or deliberately. They can get stuck in various parts of the body such as ears, nose, eyes, and respiratory tract. And most often children suffer from this.
Young children can place objects in their ears for a variety of reasons. They often play or copy the behavior of another child or adult. The objects that usually get stuck in the ear can be anything, but most often they are toys or food.
What are the symptoms of having a foreign object?
The symptoms of a foreign object in the body will depend on the location of the object.
Some common symptoms include:
- Pain: Discomfort can range from mild to severe on a pain scale.
- Copious nasal mucus: If objects enter the nose.
- Choking: If an object gets stuck in the airway, it can cause choking and symptoms such as coughing and shortness of breath.
- Breathing Problems: Object obstructing the airway may cause breathing difficulties.
How are foreign objects determined?
The diagnosis of a foreign object in the body is made through a conversation with the patient or family member to determine which object was inserted and where.
A physical examination will also be performed. In some cases, the physician may be able to see the object. X-rays can also be used to determine where a foreign object is located.
Ear drops for ear pain – Ear Infections and Hearing Loss
When ear pain occurs, it is rather difficult to independently establish an accurate diagnosis and choose ear drops suitable for treatment.
Only an otolaryngologist can quickly distinguish the symptoms of different diseases: after examination using professional equipment.
The choice of drops suitable for the treatment of a specific ear disease or closely located organs depends on what exactly caused the pathology.
If the causative agent is a fungal infection, the doctor prescribes supplements that contain a component which destroys the fungal pathogenic microflora.
By the same principle, a choice is made for inflammations of any other nature.
Otolaryngologists prescribe drops of one of four main groups – with antibiotics, antifungal, anti-inflammatory pain relievers, or agents that help remove sulfur plugs. Also in your local pharmacy you could always buy combined action supplements.
Essential Oils for Ear Infections
Well-known antiseptics – lavender and tea tree oils – can help to cope with inflammation and pain in the ears. The best way to prepare a rubbing agent is to mix these essential oils with olive oil.
Here’s a simple aromatherapy recipe for the ears: Mix 3 drops of lavender oil, 3 drops of tea tree oil, 6 drops of chamomile oil with a tablespoon of olive oil.
This is a recipe for adults. Children need a different dosage of oils.
Get Essential Oils for Ear Infections and Hearing Loss:
- Lavender Oil
- Tea Tree Oil
- Chamomile Oil
- Eucalyptus Oil
- A set of Essential Oils

If an ear pain occurs after a sore throat, then be sure to supplement the treatment with gargling of eucalyptus essential oil: mix 2 drops with half a teaspoon of baking soda or honey, then dissolve in a glass of warm water.
Even if only one ear hurts, the procedure should be done for both. To consolidate the result, continue the treatment for 2-4 days after pain relief.
How to properly rub and lotion your ears with essential oils?
An important point: the prescription remedy above, and even more so essential oils in their pure form, should not get inside the ear.
Rub the earlobes, apply the mixture behind the ear, as well as in the area of the lymph nodes on the head and neck.
Before going to bed, put a pre-squeezed cotton or gauze swab with the same product in your ear for 1-1.5 hours.
Ear Infections and Hearing Loss Final Words
Self-treatment for all ear pathologies is an incorrect solution, since the lack of qualified diagnostics and medical care can lead to an exacerbation of the disease, hearing loss, and the spread of pathology to neighboring organs.
Please Always consult your doctor before any self treatment.





