Table of Contents
Decreased Hearing: Hearing loss or Just Sulfur Plug?
Contrary to the prevailing stereotype, using cotton swabs to remove earwax is far from the best way to clean your ears.
And we are talking not only about their dubious effectiveness of using for this purpose, but also about the harm that can be done by pushing earwax into the very depths of the ear canal with your own hands or by accidentally piercing the eardrum.
Hearing loss – My Research
Mechanical damage to the inner ear can lead to hearing loss, so it is best to avoid introducing foreign objects into the ear canal.
How can You Improve your Hearing? Is this Possible To Improve at Home? Professional Advice
On the other hand, the ears need to be cleaned: otherwise, a sulfur plug can form and clog the ear canal. How can this dilemma be resolved?
What is sulfur plug?
A wax plug is a hardened accumulation of earwax that causes a blockage in the ear canal. It accumulates dirt, sweat and bacteria, so it must be removed as soon as possible. Signs of the presence of sulfuric plug include:
- Ringing and pain in the ear.
- Hearing impairment.
- Dizziness.
- Bad smell from the ear (in some cases).
With the development of pathology close to the eardrum, the patient may have a cough, migraine, coordination disturbances, sometimes nausea, accompanied by vomiting, appears.

Types of ear plugs
Sulfur plugs differ in the consistency of sulfur accumulation, they are: · Soft, which were formed relatively recently; · Dense and dry, most often they are hard and have a dark shade.
Hearing Impairment 3 Effects: Cognitive, Social, Psychological
The density of the sulfur plug directly depends on the duration of the accumulation of secretions in the ear canal. Initially, sulfur has a soft consistency, but over a period of time it becomes more dense.
Risk factors for the formation of sulfur plug include:
- OFTEN use of in-ear tablets.
- Wearing a hearing aid. Because of this, it is very important to keep your ears spotless.
- Frequent inflammatory processes, including otitis externa.
- Increased hairiness of the ear canal.
- Work in dusty areas (mine, tobacco workshops, mills).
- Age. Old age, at which physiological processes in the body change
- High humidity. This is especially true for swimmers and divers. Frequent ingestion of water in the ears leads to the swelling of the volume of sulfur, and in addition, conditions of high humidity are formed between the eardrum and the cork, which is excellent for the reproduction of microbes.
- Frequent changes in atmospheric pressure. With an increase and decrease in pressure, the eardrum bulges and retracts, which additionally provokes a thickening of the secretion.
Best Headphones for Tinnitus Sufferers (Bone Conduction Headphones Reviews and Buying Guide)
Some people, by nature, sulfur is produced in excess and is very sticky, and the hairs do not move well and do not perform the function of pushing the sulfur out of the ear.
Others are too perplexed by caring for the cleanliness of their ears and perceive the sulfur as dirt. Ear sticks are produced in sufficient quantities, but instructions on how to use them correctly are not included.
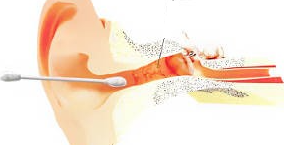
Sulfur is struggling to get out, and the lucky owner of the ear stick pushes it deeper.
In this case, the skin and delicate hairs of the ear canal are damaged by friction. And the earwax is pushed deeper inside, clogs the passage, presses on the eardrum and sticks like a tick.
How to keep your ears clean without harming them?
Ear cleaning is an essential part of your personal hygiene. But, unlike brushing your teeth and washing in the shower, this procedure does not need to be performed as often.
The movement of the lower jaw during verbal communication and food intake naturally removes the earwax. However, it is necessary to periodically clean the ear canal.
You also need to clean your ears no more than 2 times a week and you need to do this by simply blotting your ear washed under water with a clean napkin or towel.
Removal of the sulfur plug is the prerogative of the ENT doctor: he has sufficient experience and the necessary tools to perform this procedure effectively and safely. As noted above, if you wear a hearing aid, it is very important to keep it clean.
All efforts to remove earwax are meaningless if you insert a dirty hearing aid into your ear at the end of the procedure.
For these purposes, use the special cleaning kit for hearing aids, which is usually supplied with the device itself at the time of purchase. Ask a specialist to teach you this simple science
Proper hygiene of ears. Detailed Instruction
- Adhere to this rule: cleaning your ears is washing with soap to the level that your index finger reaches.
- After a bath, shower, you need to blot the ear with the tip of a towel, and remove the sulfur that is visible. This distance is roughly the tip of the little finger.
- If water gets into your ear, you need to tilt your head and blot the external ear canal with a towel.
- What is deep is dark – in no case should you go there, we can injure the eardrum and the external auditory canal.
- People with increased sulfur secretion need to visit a specialist every two to three months, the rest for prophylaxis once every six months.
P.S The use of cotton swabs helps push and tamp the earwax into the ear, which can ultimately lead to inflammation of the middle and outer ear.
Complications such as damage and perforation of the eardrum, middle ear ossicles, bleeding, and deafness are not uncommon.
In 2022, The Journal of Pediatrics reported that from 1997 to 2022. for ear injuries associated with the use of cotton swabs, 263 338 children under 18 years of age were hospitalized in hospitals
You have a sulfur plug: what to do?
If you suspect that you have a sulfur plug, seek professional help from an audiologist or otolaryngologist.
It can be difficult to identify the symptoms of this pathological condition on your own: they can be confused with signs of other diseases or not paying any attention to them at all.
If you understand that you are dealing with a sulfur plug, do not try to remove it yourself and do not put foreign objects into the ear canal in order to avoid damage to the ear structures that are sensitive to external influences.
If the presence of sulfur plug is not confirmed, then your hearing problems may be of a different nature.
How can You Improve your Hearing? Is this Possible To Improve at Home? Professional Advice
Recognition of the sulfur plug is easy with the help of otoscopy. The lumen of the ear canal is closed with a red-brown or dark brown mass.
Probing determines the soft or dense consistency of the cork. Cleansing the ear canal from the sulfuric plug is done mechanically:
- The accumulation of earwax is dissolved with special fluids and washed out of the ear canal, washing is carried out with a saline solution, less often with antiseptic agents;
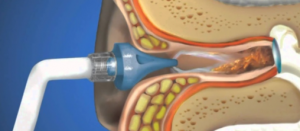
- It is possible to use a special electric pump, which will help to quickly remove the sulfur plug;
- Dry plugs are most often removed with an ear probe.
Hearing loss Final Words
Even after removing the sulfur plug, each patient will have to adhere to special recommendations that are selected individually, based on the specific condition and the presence of complications.
Most often, treatment is complemented by regular flushing of the ear canal with antiseptic compounds, taking antimicrobial drugs and other physiotherapy procedures.
In diseases of the skin of the external auditory canal, significant sloughing of the epidermis is often observed and the so-called epidermoid plug is formed, which has a dense consistency and is closely glued to the walls of the ear canal.
If experience is available, the epidermal plug is removed with a blunt hook or by washing out after preliminary instillation of salicylic alcohol.
